Question 1
Drag and drop the multicast protocol definition on the left to the correct default time interval on the right.

Answer:
+ 30 seconds: PIMv1 query interval
+ 60 seconds: IGMPv2 query interval + IGMPv1 query interval + IGMPv3 query interval
+ 120 seconds: IGMPv2 querier timeout
+ 60 seconds: IGMPv2 query interval + IGMPv1 query interval + IGMPv3 query interval
+ 120 seconds: IGMPv2 querier timeout
Question 2
Drag and drop the BGP attribute on the left to the correct category on the right.
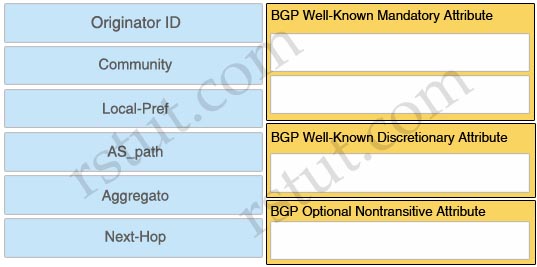
Answer:
BGP Well-Known Mandatory Attribute:
+ AS_path
+ Next-Hop
+ AS_path
+ Next-Hop
BGP Well-Known Discretionary Attribute:
+ Local-Pref
+ Local-Pref
BGP Optional Nontransitive Attribute:
+ Originator ID
+ Originator ID
Question 3
Drag and drop the items on the left to the correct category on the right.

Answer:
RADIUS:
+ Uses less memory and CPU on a router
+ Combines authentication and authorization
+ Uses less memory and CPU on a router
+ Combines authentication and authorization
TACACS+:
+ Encrypts the entire session
+ Can limit router commands based on user groups
+ Encrypts the entire session
+ Can limit router commands based on user groups
Question 4
Drag and drop the IPv6 address on the left to the correct IPv6 address type on the right.

Answer:
+ Link Local Unicast: FE80:2a5b::5
+ Global Unicast: 2005:CA75:D095::5
+ Multicast: FF01::2
+ Unique Local Unicast: FDF8:E5F3:83E4:FEAA::53
+ Global Unicast: 2005:CA75:D095::5
+ Multicast: FF01::2
+ Unique Local Unicast: FDF8:E5F3:83E4:FEAA::53
Question 5
Drag and drop the router preference on the left to the correct routing sequence (from most preferred to least preferred) on the right.

Answer:
1: Most specific prefix
2: Directly connected route
3: Static route
4: EBGP route
2: Directly connected route
3: Static route
4: EBGP route
Question 6
Drag and drop the OSPF network type on the left to the correct traffic type category on the right.

Answer:
Unicast:
+ Nonbroadcast
+ Point-to-Multipoint Nonbroadcast
+ Nonbroadcast
+ Point-to-Multipoint Nonbroadcast
Multicast:
+ Broadcast
+ Point-to-Point
+ Point-to-Multipoint
+ Broadcast
+ Point-to-Point
+ Point-to-Multipoint
Stub:
+ Loopback
+ Loopback
Question 7
What is the correct order of the VSS initialization process? drag the actions on the left to the correct initialization step on the right.

Answer:
+ initialization step 1: preparse config
+ initialization step 2: bring up VSL links
+ initialization step 3: run VSLP
+ initialization step 4: run RRP
+ initialization step 5: interchassis SSO
+ initialization step 6: continue system bootup
+ initialization step 2: bring up VSL links
+ initialization step 3: run VSLP
+ initialization step 4: run RRP
+ initialization step 5: interchassis SSO
+ initialization step 6: continue system bootup
Question 8
Drag and drop the events on the left to display the correct sequence on the right when CoPP is enabled.
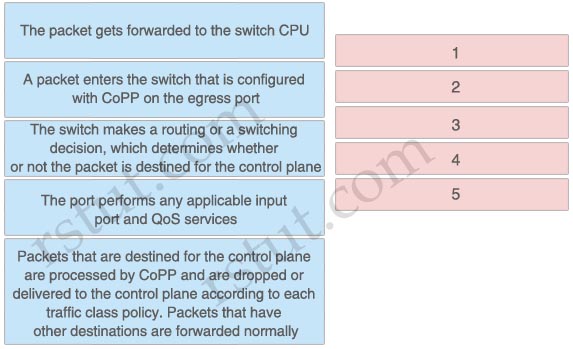
Answer:
1: A packet enters the switch that is configured with CoPP on the egress port
2: The port performs any applicable input port and QoS services.
3: The packet gets forwarded to the switch CPU
4: The switch makes a routing or a switching decision, which determines whether or not the packet is destined for the control plane
5: Packets that are destined for the control plane are processed by CoPP and are dropped or delivered to the control plane according to each traffic class policy. Packets that have other destinations are forwarded normally
2: The port performs any applicable input port and QoS services.
3: The packet gets forwarded to the switch CPU
4: The switch makes a routing or a switching decision, which determines whether or not the packet is destined for the control plane
5: Packets that are destined for the control plane are processed by CoPP and are dropped or delivered to the control plane according to each traffic class policy. Packets that have other destinations are forwarded normally
Question 9
Drag and drop the QoS requirement on the left to the correct QoS technology on the right.

Answer:
+ Police: Limits an amount of bandwidth
+ CBWFQ: Guarantees an amount of bandwidth
+ Shaping: Buffers bursting traffic
+ LLQ: Prioritizes real-time voice traffic
+ NBAR: Is an application classification
+ CBWFQ: Guarantees an amount of bandwidth
+ Shaping: Buffers bursting traffic
+ LLQ: Prioritizes real-time voice traffic
+ NBAR: Is an application classification
Question 10
Drag and drop the IPv6 multicast feature or protocol on the left to the correct address space on the right.
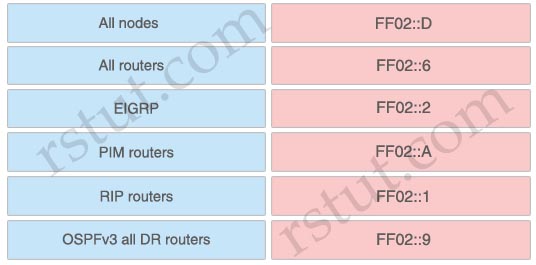
Answer:
+ FF02::D: PIM routers
+ FF02::6: OSPFv3 all DR routers
+ FF02::2: All routers
+ FF02::A: EIGRP
+ FF02::1: All nodes
+ FF02::9: RIP routers
+ FF02::6: OSPFv3 all DR routers
+ FF02::2: All routers
+ FF02::A: EIGRP
+ FF02::1: All nodes
+ FF02::9: RIP routers
Question 11
Drag and drop the IPv6 multicast feature or protocol on the left to the correct address space on the right.
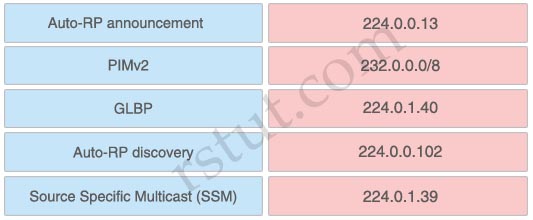
Answer:
+ 224.0.0.13: PIMv2
+ 232.0.0.0/8: Source Specific Multicast (SSM)
+ 224.0.1.40: Auto-RP discovery
+ 224.0.0.102: GLBP
+ 224.0.1.39: Auto-RP announcement
+ 232.0.0.0/8: Source Specific Multicast (SSM)
+ 224.0.1.40: Auto-RP discovery
+ 224.0.0.102: GLBP
+ 224.0.1.39: Auto-RP announcement
Sign up here with your email

ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon