IS-IS Questions
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit.
| RouterA# conf t router isis 1 net 49.5200.1580.3500.6002.00
RouterB#
conf t router isis 1 net 49.5200.1580.3500.6002.00 |
Router A and router B are physically connected over an Ethernet interface, and ISIS is configured as shown. Which option explains why the ISIS neighborship is not getting formed between router A and router B?
A. same area ID
B. same N selector
C. same domain ID
D. same system ID
B. same N selector
C. same domain ID
D. same system ID
Answer: D
Question 2
Which three statements about IS-IS are true? (Choose three)
A. IS-IS can be used only in the service provider network.
B. IS-IS can be used to route both IP and CLNP.
C. IS-IS has three different levels of authentication: interface level, process level, and domain level.
D. IS-IS is an IETF standard.
E. IS-IS has the capability to provide address summarization between areas.
B. IS-IS can be used to route both IP and CLNP.
C. IS-IS has three different levels of authentication: interface level, process level, and domain level.
D. IS-IS is an IETF standard.
E. IS-IS has the capability to provide address summarization between areas.
Answer: B C E
Question 3
Which three elements compose a network entity title? (Choose three)
A. area ID
B. domain ID
C. system ID
D. NSAP selector
E. MAC address
F. IP address
B. domain ID
C. system ID
D. NSAP selector
E. MAC address
F. IP address
Answer: A C D
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.
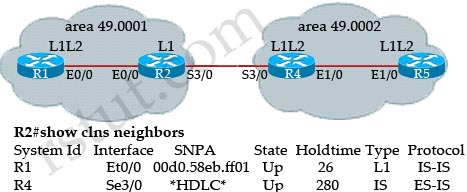
Why is the neighbor relationship between R2 and R4 shown as ES-IS?
A. because there is an MTU mismatch between R2 and R4
B. because interface S3/0 of R4 is configured as L1/L2
C. because interface S3/0 of R2 is configured as L1
D. because there is a hello interval mismatch between R2 and R4
B. because interface S3/0 of R4 is configured as L1/L2
C. because interface S3/0 of R2 is configured as L1
D. because there is a hello interval mismatch between R2 and R4
Answer: C
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.
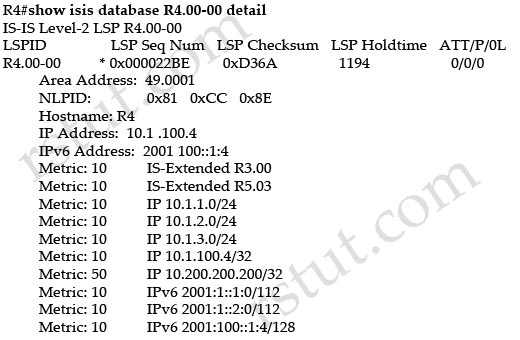
Which statement is true?
A. IS-IS has been enabled on R4 for IPv6, single-topology.
B. IS-IS has been enabled on R4 for IPv6, multitopology.
C. IS-IS has been enabled on R4 for IPv6, single-topology and multitopology.
D. R4 advertises IPv6 prefixes, but it does not forward IPv6 traffic, because the protocol has not been enabled under router IS-IS.
B. IS-IS has been enabled on R4 for IPv6, multitopology.
C. IS-IS has been enabled on R4 for IPv6, single-topology and multitopology.
D. R4 advertises IPv6 prefixes, but it does not forward IPv6 traffic, because the protocol has not been enabled under router IS-IS.
Answer: A
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit.
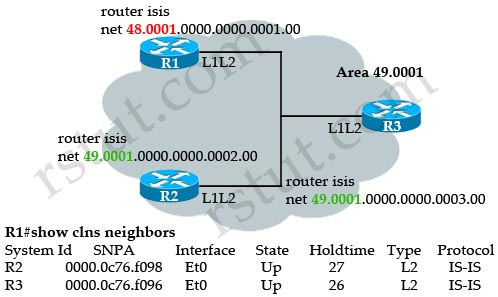
Why is the neighbor relationship between R1 & R2 and R1 & R3 an L2-type neighborship?
A. because the area ID on R1 is different as compared to the area ID of R2 and R3
B. because the circuit type on those three routers is L1/L2
C. because the network type between R1, R2, and R3 is point-to-point
D. because the hello interval is not the same on those three routers
B. because the circuit type on those three routers is L1/L2
C. because the network type between R1, R2, and R3 is point-to-point
D. because the hello interval is not the same on those three routers
Answer: A
Question 7
With which ISs will an ISIS Level 1 IS exchange routing information?
A. Level 1 ISs
B. Level 1 ISs in the same area
C. Level 1 and Level 2 ISs
D. Level 2 ISs
B. Level 1 ISs in the same area
C. Level 1 and Level 2 ISs
D. Level 2 ISs
Answer: B
Question 8
Which three statements about the designated router election in IS-IS are true? (Choose three)
A. If the IS-IS DR fails, a new DR is elected.
B. The IS-IS DR will preempt. If a new router with better priority is added, it just becomes active in the network.
C. If there is a tie in DR priority, the router with a higher IP address wins.
D. If there is a tie in DR priority, the router with a higher MAC address wins.
E. If the DR fails, the BDR is promoted as the DR.
F. The DR is optional in a point-to-point network.
B. The IS-IS DR will preempt. If a new router with better priority is added, it just becomes active in the network.
C. If there is a tie in DR priority, the router with a higher IP address wins.
D. If there is a tie in DR priority, the router with a higher MAC address wins.
E. If the DR fails, the BDR is promoted as the DR.
F. The DR is optional in a point-to-point network.
Answer: A B D
Sign up here with your email

ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon