Multicast Questions
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit.
| R4 interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 ip pim sparse-dense-mode duplex auto speed auto standby 1 ip 192.168.2.4 standby 1 priority 150 standby 1 preempt R5 interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 ip pim sparse-dense-mode duplex auto speed auto standby 1 ip 192.168.2.4 |
The interface FastEthernet0/1 of both routers R4 and R5 is connected to the same Ethernet segment with a multicast receiver. Which two statements are true? (Choose two)
A. Multicast traffic that is destined to a receiver with IP address 192.168.2.6 will flow through router R4.
B. Both routers R4 and R5 will send PIM join messages to the RP.
C. Only router R5 will send a multicast join message to the RP.
D. Multicast traffic that is destined to a receiver with IP address 192.168.2.6 will flow through router R5.
B. Both routers R4 and R5 will send PIM join messages to the RP.
C. Only router R5 will send a multicast join message to the RP.
D. Multicast traffic that is destined to a receiver with IP address 192.168.2.6 will flow through router R5.
Answer: C D
Question 2
Which technology can be used to prevent flooding of IPv6 multicast traffic on a switch?
A. IGMP snooping
B. IGMP filtering
C. MLD snooping
D. MLD filtering
B. IGMP filtering
C. MLD snooping
D. MLD filtering
Answer: C
Question 3
Which two statements are true about IPv6 multicast? (Choose two)
A. Receivers interested in IPv6 multicast traffic use IGMPv6 to signal their interest in the IPv6 multicast group.
B. The PIM router with the lowest IPv6 address becomes the DR for the LAN.
C. An IPv6 multicast address is an IPv6 address that has a prefix of FF00::/8.
D. The IPv6 all-routers multicast group is FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:2.
B. The PIM router with the lowest IPv6 address becomes the DR for the LAN.
C. An IPv6 multicast address is an IPv6 address that has a prefix of FF00::/8.
D. The IPv6 all-routers multicast group is FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:2.
Answer: C D
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.

Which two statements about the device that generated the output are true? (Choose two)
A. The SPT-bit is set.
B. The sparse-mode flag is set.
C. The RP-bit is set.
D. The source-specific host report was received.
B. The sparse-mode flag is set.
C. The RP-bit is set.
D. The source-specific host report was received.
Answer: A D
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.

Which three statements about the output are true? (Choose three)
A. This switch is currently receiving a multicast data stream that is being forwarded out VLAN 150.
B. A multicast receiver has requested to join one or more of the multicast groups.
C. Group 224.0.1.40 is a reserved address, and it should not be used for multicast user data transfer.
D. One or more multicast groups are operating in PIM dense mode.
E. One or more of the multicast data streams will be forwarded out to neighbor 10.85.20.20.
F. Group 239.192.1.1 is a reserved address, and it should not be used for multicast user data transfer.
B. A multicast receiver has requested to join one or more of the multicast groups.
C. Group 224.0.1.40 is a reserved address, and it should not be used for multicast user data transfer.
D. One or more multicast groups are operating in PIM dense mode.
E. One or more of the multicast data streams will be forwarded out to neighbor 10.85.20.20.
F. Group 239.192.1.1 is a reserved address, and it should not be used for multicast user data transfer.
Answer: A B C
Question 6
Which statement is true about IGMP?
A. Multicast sources send IGMP messages to their first-hop router, which then generates a PIM join message that is then sent to the RP.
B. Multicast receivers send IGMP messages to their first-hop router, which then forwards the IGMP messages to the RP.
C. IGMP messages are encapsulated in PIM register messages and sent to the RP.
D. Multicast receivers send IGMP messages to signal their interest to receive traffic for specific multicast groups.
B. Multicast receivers send IGMP messages to their first-hop router, which then forwards the IGMP messages to the RP.
C. IGMP messages are encapsulated in PIM register messages and sent to the RP.
D. Multicast receivers send IGMP messages to signal their interest to receive traffic for specific multicast groups.
Answer: D
Question 7
Where is multicast traffic sent, when it is originated from a spoke site in a DMVPN phase 2 cloud?
A. spoke-spoke
B. nowhere, because multicast does not work over DMVPN
C. spoke-spoke and spoke-hub
D. spoke-hub
B. nowhere, because multicast does not work over DMVPN
C. spoke-spoke and spoke-hub
D. spoke-hub
Answer: D
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit.
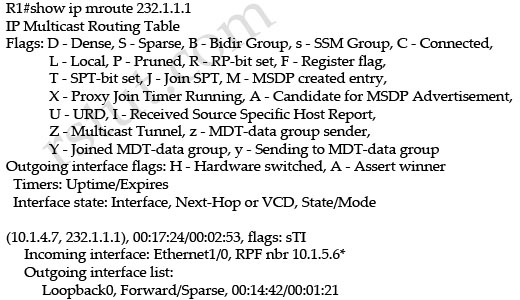
What is the meaning of the asterisk (*) in the output?
A. PIM neighbor 10.1.5.6 is the RPF neighbor for the group 232.1.1.1 for the shared tree.
B. PIM neighbor 10.1.5.6 is the one that is seen as the RPF neighbor when performing the command show ip rpf 10.1.4.7.
C. PIM neighbor 10.1.5.6 is the winner of an assert mechanism.
D. The RPF neighbor 10.1.5.6 is invalid.
B. PIM neighbor 10.1.5.6 is the one that is seen as the RPF neighbor when performing the command show ip rpf 10.1.4.7.
C. PIM neighbor 10.1.5.6 is the winner of an assert mechanism.
D. The RPF neighbor 10.1.5.6 is invalid.
Answer: C
Sign up here with your email

ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon