Here you will find answers to IP Services Questions
Question 1
What is the default stratum clock on a Cisco router, when you see the key word “master” configured on the NTP line?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 6
E. 8
B. 2
C. 4
D. 6
E. 8
Answer: E
Explanation
The “ntp master” is used to configure the device as a master clock when external time synchronization is not possible; for example, the router is not connected to the Internet.
If the network has ntp master configured and it cannot reach any clock with a lower stratum number, the system claims to be synchronized at the configured stratum number, and other systems synchronize to it via NTP. By default, the master clock function is disabled. When enabled, the default stratum is 8.
In the world of NTP, stratum levels define the distance from the reference clock. A reference clock is a stratum-0 device that is assumed to be accurate and has little or no delay associated with it (typically an atomic clock). A server that is directly connected to a stratum-0 device is called a stratum-1 server, a server that is directly connected to a stratum-1 is called a stratum-2 server and so on.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps1893/products_command_reference_chapter09186a008007dec6.html)
Question 2
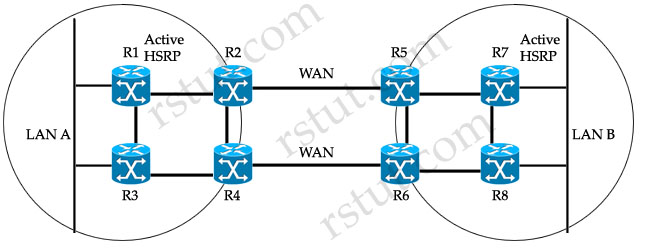
Refer to the exhibit. There are two sites connected across WAN links. All intersite and intrasite links always have the same routing metric. The network administrator sees only the top routers and links being used by hosts at both LAN A and LAN B. What would be two suggestions to load-balance the traffic across both WAN links? (Choose two)
A. Make HSRP track interfaces between the edge and core routers.
B. Replace HSRP with GLBP.
C. Add crossed intrasite links: R1-R4, R2-R3, R5-R8, and R6-R7.
D. Make R3 and R8 have lower HSRP priority than R1 and R7.
E. Replace HSRP with VRRP.
B. Replace HSRP with GLBP.
C. Add crossed intrasite links: R1-R4, R2-R3, R5-R8, and R6-R7.
D. Make R3 and R8 have lower HSRP priority than R1 and R7.
E. Replace HSRP with VRRP.
Answer: B C
Explanation
The administrator sees only the top routers (R1,R2,R5 & R7) and links being used by hosts at both LAN A and LAN B because R1 & R7 are currently active HSRP routers (notice that all the data will need to go through these routers). Next, all intersite and intrasite links have the same routing metric so these active routers will send packets to R2 or R5, not R3, R4, R6 or R8 because of the lower metric of the top routers. For example, hosts in LAN A want to send data to hosts in LAN B, they will send data to R1 -> R2 -> R5 -> R7, which has lower metric than the path R1 -> R3 -> R4 -> R6 -> R5 (or R8) -> R7.
To make the network better, we should add crossed intrasite links so that R1 & R7 can send data to both R2/R4 & R5/R6 as they have the same routing metric now -> C is correct.
Cisco Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) differs from Cisco Hot Standby Redundancy Protocol (HSRP) and IETF RFC 3768 Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) in that it has the ability to load balance over multiple gateways. Like HSRP and VRRP an election occurs, but rather than a single active router winning the election, GLBP elects an Active Virtual Gateway (AVG) to assign virtual MAC addresses to each of the other GLBP routers and to assign each network host to one of the GLBP routers -> B is correct.
Note: The routers that receive this MAC address assignment are known as Active Virtual Forwarders (AVF).
Note: The routers that receive this MAC address assignment are known as Active Virtual Forwarders (AVF).
Sign up here with your email

ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon