Here you will find answers to Security Questions
Question 1
Which of these is mandatory when configuring Cisco IOS Firewall?
A. Cisco IOS IPS enabled on the untrusted interface
B. NBAR enabled to perform protocol discovery and deep packet inspection
C. a route map to define the trusted outgoing traffic
D. a route map to define the application inspection rules
E. an inbound extended ACL applied to the untrusted interface
B. NBAR enabled to perform protocol discovery and deep packet inspection
C. a route map to define the trusted outgoing traffic
D. a route map to define the application inspection rules
E. an inbound extended ACL applied to the untrusted interface
Answer: E
Question 2
If a certificate authority trustpoint is not configured when enabling HTTPS and the remote HTTPS server requires client authentication, connections to the secure HTTP client will fail. Which command must be enabled for correct operation?
A. ip http client secure-ciphersuite 3des-ede-cbc-sha
B. ip https max-connections 10
C. ip http timeout-policy idle 30 life 120 requests 100
D. ip http client secure-trustpoint trustpoint-name
B. ip https max-connections 10
C. ip http timeout-policy idle 30 life 120 requests 100
D. ip http client secure-trustpoint trustpoint-name
Answer: D
Question 3
Which two of these elements need to be configured prior to enabling SSH? (Choose two)
A. hostname
B. loopback address
C. default gateway
D. domain name
E. SSH peer address
B. loopback address
C. default gateway
D. domain name
E. SSH peer address
Answer: A D
Explanation
A hostname and a domain name were required to generate the keys, since router uses its fully qualified domain name (FQDN) as the label of the key pair.
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is the complete domain name for a specific computer, or host, on the Internet. The FQDN consists of two parts: the hostname and the domain name. For example, an FQDN for a mail server might be myemail.rstut.com. The hostname is “myemail”, and the host is located within the domain “rstut.com”.
Set a host name
hostname myemail
hostname myemail
Set a ip domain name
ip domain-name rstut.com
ip domain-name rstut.com
Question 4
Spoofing attack is increasingly more common and becoming more sophisticated. Which Cisco IOS feature can provide protection against spoofing attacks?
A. lock-any-key ACL and/or reflexive ACL
B. TCP Intercept
C. IP Source Guard and/or Unicast RPF
D. Cisco IOS Firewall (CBAC)
B. TCP Intercept
C. IP Source Guard and/or Unicast RPF
D. Cisco IOS Firewall (CBAC)
Answer: C
Explanation
IP spoofing is a situation in which an intruder uses the IP address of a trusted device in order to gain access to your network.
IP Source Guard tracks the IP addresses of the host connected to each port and prevents traffic sourced from another IP address from entering that port. The tracking can be done based on just an IP address or on both IP and MAC addresses.
The Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding feature (Unicast RPF) helps the network guard against “spoofed” IP packets passing through a router. A spoofed IP address is one that is manipulated to have a forged IP source address. Unicast RPF enables the administrator to drop packets that lack a verifiable source IP address at the router. Note how similar this is to the Reverse Path Forwarding check with multicast traffic. In that case, traffic was dropped to avoid loops.
Question 5
Which is the result of enabling IP Source Guard on an untrusted switch port that does not have DHCP snooping enabled?
A. DHCP requests will be switched in the software, which may result in lengthy response times.
B. The switch will run out of ACL hardware resources.
C. All DHCP requests will pass through the switch untested.
D. The DHCP server reply will be dropped and the client will not be able to obtain an IP address.
B. The switch will run out of ACL hardware resources.
C. All DHCP requests will pass through the switch untested.
D. The DHCP server reply will be dropped and the client will not be able to obtain an IP address.
Answer: D
Explanation
DHCP snooping is a feature that provides network security by filtering untrusted DHCP messages and by building and
maintaining a DHCP snooping binding database. DHCP snooping acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and DHCP servers. DHCP snooping allows all DHCP messages on trusted ports, but it filters DHCP messages on untrusted ports.
maintaining a DHCP snooping binding database. DHCP snooping acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and DHCP servers. DHCP snooping allows all DHCP messages on trusted ports, but it filters DHCP messages on untrusted ports.
Let’s see an example without DHCP snooping.
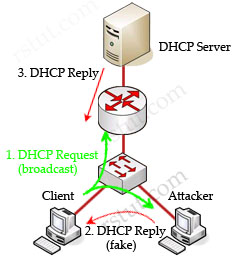
In this example, a client is trying to get a valid IP address from the DHCP Server. It sends out a DHCP Request (broadcast) message so both the DHCP Server and the Attacker can hear it. The attacker pretends to be a DHCP Server and replies to the request with a valid IP address but using its own IP address as the default gateway. If its reply can arrive before the real DHCP reply, it will be considered the default gateway. From now, the client will send packets to the attacker as it believes the attacker is the default gateway. The attacker captures these packets and sends a copy to the desired default gateway -> it becomes a “man in the middle”.
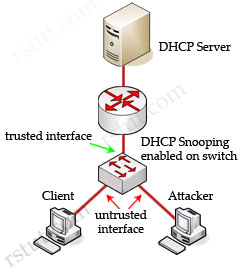
Cisco switches can use DHCP snooping feature to mitigate this type of attack. When DHCP snooping is enabled, switch ports are classified as trusted or untrusted. Trusted ports are allowed to send all types of DHCP messages while untrusted ports can send only DHCP requests. If a DHCP reply is seen on an untrusted port, the port is shut down.
By default, if you enable IP source guard without any DHCP snooping bindings on the port, a default port access-list (PACL) that denies all IP traffic expect the DHCP Request (DHCP Discover) is installed on the port. Therefore the DHCP Server can hear the DHCP Request from the Client but its reply is filtered by the switch and the client can’t obtain an IP address -> D is correct.
Some useful information about DHCP snooping & IP Source Guard:
When enabled along with DHCP snooping, IP Source Guard checks both the source IP and source MAC addresses against the DHCP snooping binding database (or a static IP source entry). If the entries do not match, the frame is filtered. For example, assume that the show ip dhcp snooping binding command displays the following binding table entry:
| MacAddress | IpAddress | LeaseSec | Type | VLAN | Interface |
| 01:25:4A:5E:6D:25 | 10.0.0.20 | 6943 | dhcp-snooping | 2 | FastEthernet0/1 |
If the switch receives an IP packet with an IP address of 10.0.0.20, IP Source Guard forwards the packet only if the MAC address of the packet is 01:25:4A:5E:6D:25.
Sign up here with your email

ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon