Question 1
Which two statements about private VLANs are true? (Choose two)
A. Only one isolated VLAN can be mapped to a primary VLAN.
B. Only one community VLAN can be mapped to a primary VLAN.
C. Multiple isolated VLANs can be mapped to a primary VLAN.
D. Multiple community VLANs can be mapped to a primary VLAN.
B. Only one community VLAN can be mapped to a primary VLAN.
C. Multiple isolated VLANs can be mapped to a primary VLAN.
D. Multiple community VLANs can be mapped to a primary VLAN.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The main purpose of Private VLAN (PVLAN) is to provide the ability to isolate hosts at Layer 2 instead of Layer 3. As you know, a VLAN is a broadcast domain, by using PVLAN we are splitting that domain into some smaller broadcast domains. For example, without PVLAN, a service provider wants to increase security by isolating customers into separate domains so that they can’t access each other, they have to assign them into different VLANs and use different subnets. This can result in a waste of IP addresses and difficulty in VLAN management. Private VLANs (PVLANs) can solve this problem by allowing the isolation of devices at Layer 2 in the same subnet. PVLAN can be considered “VLANs inside VLAN”.
There are three types of ports in PVLAN:
* Isolated: only communicate with promiscuous ports. Notice that it cannot even communicate with another isolated port. Also, there can be only 1 isolated VLAN per PVLAN.
* Promiscuous: can communicate with all other ports. The default gateway is usually connected to this port so that all devices in PVLAN can go outside.
* Community: can communicate with other members of that community and promiscuous ports but cannot communicate with other communities. There can be multiple community VLANs per PVLAN.
There are three types of ports in PVLAN:
* Isolated: only communicate with promiscuous ports. Notice that it cannot even communicate with another isolated port. Also, there can be only 1 isolated VLAN per PVLAN.
* Promiscuous: can communicate with all other ports. The default gateway is usually connected to this port so that all devices in PVLAN can go outside.
* Community: can communicate with other members of that community and promiscuous ports but cannot communicate with other communities. There can be multiple community VLANs per PVLAN.
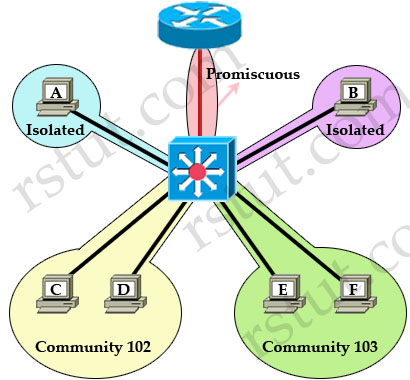
For example, in the topology above:
+ Host A cannot communicate with Host B, C, D, E and F. It can only communicate with Promiscuous port to the router. Notice that even two Isolated ports in the same VLAN cannot communicate with each other.
+ Host C can communicate with Host D because they are in the same community but Host C cannot communicate with E and F because they are in a different community.
+ All hosts can go outside through promiscuous port.
Also I want to mention about the concept of “primary VLAN” and “secondary VLAN”. PVLAN can have only one primary VLAN; all VLANs in a PVLAN domain share the same primary VLAN. Secondary VLANs are isolated or community VLANs.
+ Host A cannot communicate with Host B, C, D, E and F. It can only communicate with Promiscuous port to the router. Notice that even two Isolated ports in the same VLAN cannot communicate with each other.
+ Host C can communicate with Host D because they are in the same community but Host C cannot communicate with E and F because they are in a different community.
+ All hosts can go outside through promiscuous port.
Also I want to mention about the concept of “primary VLAN” and “secondary VLAN”. PVLAN can have only one primary VLAN; all VLANs in a PVLAN domain share the same primary VLAN. Secondary VLANs are isolated or community VLANs.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit.
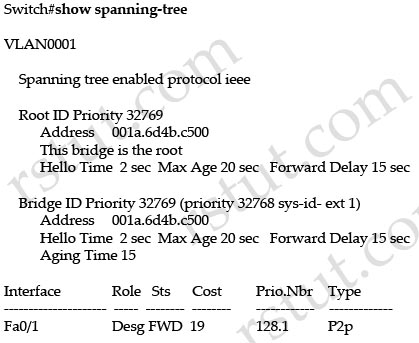
If you change the Spanning Tree Protocol from pvst to rapid-pvst, what is the effect on the interface Fa0/1 port state?
A. It transitions to the listening state, and then the forwarding state.
B. It transitions to the learning state and then the forwarding state.
C. It transitions to the blocking state, then the learning state, and then the forwarding state.
D. It transitions to the blocking state and then the forwarding state.
B. It transitions to the learning state and then the forwarding state.
C. It transitions to the blocking state, then the learning state, and then the forwarding state.
D. It transitions to the blocking state and then the forwarding state.
Answer: C
Sign up here with your email

ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon