Here you will find answers to Switching Basics Questions
Question 1
What two features in Cisco switches help prevent Layer 2 loops? (Choose two)
A. UniDirectional Link Detection
B. Hot Standby Router Protocol
C. Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
D. PortFast
E. root guard
F. loop guard
B. Hot Standby Router Protocol
C. Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
D. PortFast
E. root guard
F. loop guard
Answer: A F
Explanation
Both UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD) and Loop Guard protect a switch trunk port from causing loops. Both features prevent switch ports from errantly moving from a blocking to a forwarding state when a unidirectional link exists in the network.
Unidirectional links are simply links for which one of the two transmission paths on the link has failed, but not both. This can happen as a result of miscabling, cutting one fiber cable, unplugging one fiber, GBIC problems, or other reasons
UDLD – Uses Layer 2 messaging to decide when a switch can no longer receive frames from a neighbor. The switch whose transmit interface did not fail is placed into an err-disabled state.
Loop Guard – When normal BPDUs are no longer received, the port does not go through normal STP convergence, but rather falls into an STP loop-inconsistent state.
(Reference: CCIE Routing and Switching Exam Certification Guide)
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. Which switching feature is being tested?
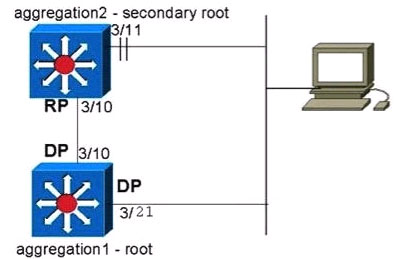
aggregation-2 (enable) set spantree portfast 3/11 ena
Waning Spantree port fast start should only be enabled on ports connected to a single host.
Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc. to a fast start port can cause temporary spannmg tree loops. Use with caution.
Spantree port 3/11 fast start enabled.
aggregation-2 (enable) set spantree portfast bpdu-filter ena
Spantree portfast bpdu-filter enabled on this switch.
2001 Feb 06 13:32:14 %SPANTREE-4-LOOPGUARDBLOCK: No BPDUs were received on port 3/21 m VLAN 99. Moved to loop inconsistent state
Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc. to a fast start port can cause temporary spannmg tree loops. Use with caution.
Spantree port 3/11 fast start enabled.
aggregation-2 (enable) set spantree portfast bpdu-filter ena
Spantree portfast bpdu-filter enabled on this switch.
2001 Feb 06 13:32:14 %SPANTREE-4-LOOPGUARDBLOCK: No BPDUs were received on port 3/21 m VLAN 99. Moved to loop inconsistent state
A. loop guard
B. PortFast
C. root guard
D. BDPU guard
B. PortFast
C. root guard
D. BDPU guard
Answer: A
Question 3
Which three of these statements about Dynamic Trunking Protocol are correct? (Choose three)
A. It supports autonegotiation for both ISL and IEEE 802.1 Q trunks.
B. It must be disabled on an interface if you do not want the interface to work as a trunk or start negotiation to become a trunk.
C. It is a point-to-multipoint protocol.
D. It is a point-to-point protocol.
E. It is not supported on private VLAN ports or tunneling ports.
B. It must be disabled on an interface if you do not want the interface to work as a trunk or start negotiation to become a trunk.
C. It is a point-to-multipoint protocol.
D. It is a point-to-point protocol.
E. It is not supported on private VLAN ports or tunneling ports.
Answer: A B D
Question 4
You are designing your network to be able to use trunks. As part of this process you are comparing the ISL and 802.1 Q encapsulation options. All of these statements about the two encapsulation options are correct except which one?
A. Both support normal and extended VLAN ranges.
B. ISL is a Cisco proprietary encapsulation method and 802.1 Q is an IEEE standard.
C. ISL encapsulates the original frame.
D. Both support native VLANs.
E. 802.1 Q does not encapsulate the original frame.
B. ISL is a Cisco proprietary encapsulation method and 802.1 Q is an IEEE standard.
C. ISL encapsulates the original frame.
D. Both support native VLANs.
E. 802.1 Q does not encapsulate the original frame.
Answer: D
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. From the MAC addresses shown in the command output, to which two ports is the multicast stream 225.230.57.199 being forwarded on this switch? (Choose two)
Switch#show mac-address-table multicast
| vlan | mac address | type | ports |
| —————–+ | ——————————+ | ———————+ | —————————————————————– |
| 2 2 2 3 3 | 0100.5ee6.39c7 0100.5e00.0123 0100.5e66.39c7 0100.5e00.017f 0100.5e50.4453 | igmp igmp igmp igmp igmp | Gi3/7,Fa6/28,Fa7/20 Fa5/7,Fa6/28,Fa7/20 Gi3/4,Gi3/7,Fa4/10,Fa4/14,Fa7/31,Fa7/40 Gi3/7,Fa6/21 Gi3/7,Fa4/2,Fa4/3,Fa4/14,Fa4/38,Fa5/3 |
A. Fa6/28
B. Fa7/20
C. Gi3/7
D. Fa4/2
E. Fa4/14
F. Fa4/38
G. Fa6/28
H. Fa5/7
B. Fa7/20
C. Gi3/7
D. Fa4/2
E. Fa4/14
F. Fa4/38
G. Fa6/28
H. Fa5/7
Answer: C E
Question 6
You are about to migrate a customer network to use a VSS. Which of these statements is true about a VSS?
A. The VSS switch must be the root bridge for all VLANs and is automatically designated.
B. The VSS switch is defined in RFC 4318 as a managed object.
C. The PAgP+ or LACP protocols are used to maintain the operational state of the VSS devices.
D. A VSS interoperates with a virtual port channel.
E. The 802.1Q or ISL protocols are used to maintain the operational state of the VSS devices.
F. A VSS increases the size of the spanning-tree domain.
B. The VSS switch is defined in RFC 4318 as a managed object.
C. The PAgP+ or LACP protocols are used to maintain the operational state of the VSS devices.
D. A VSS interoperates with a virtual port channel.
E. The 802.1Q or ISL protocols are used to maintain the operational state of the VSS devices.
F. A VSS increases the size of the spanning-tree domain.
Answer: C
Explanation
Virtual switching system (VSS) is a network system virtualization technology that pools multiple Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches into one virtual switch, increasing operational efficiency, boosting nonstop communications, and scaling system bandwidth capacity to 1.4 Tbps. At the initial phase, a VSS will allow two physical Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches to operate as a single logical virtual switch called a virtual switching system 1440 (VSS1440)

Virtual Switching System 1440 Compared to Traditional Network Design
C is the correct answer as in the recommendations of the above link, the author wrote:
Do not use on and off options with PAgP or LACP or Trunk protocol negotiation.
* PAgP — Run Desirable-Desirable with MEC links.
* LACP — Run Active-Active with MEC links.
* Trunk — Run Desirable-Desirable with MEC links.
* LACP — Run Active-Active with MEC links.
* Trunk — Run Desirable-Desirable with MEC links.
Recommended link: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/switches/ps5718/ps9336/prod_qas0900aecd806ed74b.html
Question 7
An 802.1 Q trunk is not coming up between two switches. The ports on both switches are configured as “switchport mode desirable.” Assuming that there is no physical issue, choose two possible causes. (Choose two.)
A. Incorrect VTP domain
B. Incorrect VTP password
C. Incorrect VTP mode
D. Incorrect VTP configuration revision
A. Incorrect VTP domain
B. Incorrect VTP password
C. Incorrect VTP mode
D. Incorrect VTP configuration revision
Answer: A B
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. Look at the command output. Assume that there is no other path, and the configuration is correct. What would be the consequences of this situation?
Switch1#show cdp neighbor
Capability Codes: R – Router, T- Trans Bridge, B – Source Route Bridge S – Switch, H – Host, I – IGMP, r- Repeater, P – Phone
Capability Codes: R – Router, T- Trans Bridge, B – Source Route Bridge S – Switch, H – Host, I – IGMP, r- Repeater, P – Phone
| Device ID | Local Intrfce | Holdtme | Capability | Platform | Port ID |
| Switch2 | Gig 1/0/3 | 160 | S I | WS-C2955C | Fas0/13 |
Switch2#show cdp neighbor
Capability Codes: R – Router, T- Trans Bridge, B – Source Route Bridge S – Switch, H – Host, I – IGMP, r- Repeater, P – Phone
| Device ID | Local Intrfce | Holdtme | Capability | Platform | Port ID |
| Switch1 | Fas0/13 | 173 | R S I | WS-C3750G | Gig1/0/4 |
A. Users in SW1 can ping SW2 but not vice versa.
B. Users in SW2 can ping SW1 but not vice versa.
C. Users in SW1 and SW2 can ping each other.
D. Users in SW1 and SW2 cannot ping each other.
B. Users in SW2 can ping SW1 but not vice versa.
C. Users in SW1 and SW2 can ping each other.
D. Users in SW1 and SW2 cannot ping each other.
Answer: D
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. Look at the command output. What can you use to prevent this behavior?
Switch 1#show cdp neighbors
Capability Codes: R – Router, T – Trans Bridge, B – Source Route Bridge S – Switch, H – Host, I – IGMP, r – Repeater
Capability Codes: R – Router, T – Trans Bridge, B – Source Route Bridge S – Switch, H – Host, I – IGMP, r – Repeater
| Device ID | Local Intrfce | Holdtme | Capability | Platform | Port ID |
| Switch2 | Gig 1/0/3 | 160 | S I | WS-C2955C | Fas0/13 |
Switch 1#
Switch2#show cdp neighbor
Capability Codes: R – Router, T- Trans Bridge, B – Source Route Bridge S – Switch, H – Host, I – IGMP, r- Repeater
| Device ID | Local Intrfce | Holdtme | Capability | Platform | Port ID |
| Switch1 | Fas0/13 | 173 | R S I | WS-C3750G | Gig1/0/4 |
A. UDLD
B. spanning-tree loopguard
C. VTP mode transparent
D. switchport mode desirable
B. spanning-tree loopguard
C. VTP mode transparent
D. switchport mode desirable
Answer: A
Sign up here with your email

ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon